

The other fragment falls at a distance of 1.375R from the point of launching. If the origin is fixed to the final position of the center of mass, the principle of moments holds good. After the fragments have fallen on the ground, the center of mass rests at a distance R (the range) from the point of projection as shown in the diagram. After the explosion, the center of mass of the projectile will continue to complete the parabolic path even though the fragments are not following the same parabolic path. It is an explosion of its own without any external influence.

Where will the other fragment fall? Solution One fragment of mass 3 kg falls at three fourth of the range R of the projectile. The negative signs in the two answers indicate the opposite direction of the boat with respect to the stationary observer and the walking man on the boat.Ī projectile of mass 5 kg, in its course of motion explodes on its own into two fragments. The magnitude of the relative velocity of the boat with respect to the walking man is greater than the magnitude of the relative velocity of the boat with respect to the stationary observer. The negative sign in the answer implies that the boat appears to move in the opposite direction to the man walking in the boat. Where, v 21 is the relative velocity of the boat with respect to the walking man. (ii) To determine the velocity of the boat with respect to the walking man: The negative sign in the answer implies that the boat moves in a direction opposite to that of the walking man on the boat to a stationary observer on land. Hence, the velocity of the center of mass is zero (v CM = 0). The man moves with a velocity, v 1 = 2 m s -1 and the boat moves with a velocity v 2 (which is to be found) (i) To determine the velocity of the boat with respect to a stationary observer on land:Īs there is no external force acting on the system, the man and boat move due to the friction, which is an internal force in the boat-man system. What will be the velocity of the boat, (a) with respect to the stationary observer on land? (b) with respect to the man walking in the boat? He walks towards the other end of the boat with a constant velocity of 2 ms -1 with respect to a stationary observer on land. Solved Example Problems for Motion of Center of MassĪ man of mass 50 kg is standing at one end of a boat of mass 300 kg floating on still water. If, the small disc is removed concentrically from the large disc, what will be the position of the center of mass of the remaining portion of disc? The center of mass of the remaining portion is at a distance R/6 to the left from the center of the disc. mass per unit surface area), σ=M/πR 2 then, the mass m of small disc is, We can write from the principle of moments, Hence, the remaining portion of the disc should have its center of mass to the left of the origin say, at a distance x. Let the mass of the small disc cut and removed be m and its center of mass is at a position R/2 to the right of the origin as shown in the figure. Its center of mass would be at the geometric center of the disc on which the origin coincides.
#MASS FORMULA PHYSICS FULL#
Let us consider the mass of the uncut full disc be M. Find the center of mass of the remaining portion of the disc. When we compare case (i) with case (ii), the x CM = 2.5m from 3 kg mass could also be obtained by subtracting 4 m (the position of 3 kg mass) from 6.5 m, where the center of mass was located in case (i)įrom a uniform disc of radius R, a small disc of radius R/2 is cut and removed as shown in the diagram.
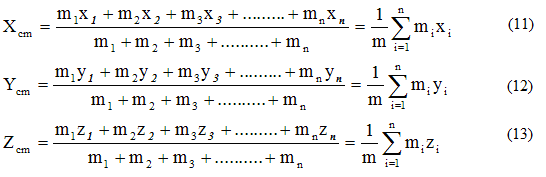
If the origin is shifted to the center of mass, then the principle of moments holds good.

This result shows that the center of mass is located closer to larger mass. The center of mass is located 2.5 m from 3 kg point mass, (and 1.5 m from the 5 kg point mass) on X-axis. The position of 3 kg point mass is zero (x 1 = 0) and the position of 5 kg point mass is 4 m from the shifted origin (x 2 = 4 m). The origin is shifted to 3 kg mass along X-axis. (ii) To find the center of mass from 3 kg mass: The center of mass is located 6.5 m from the origin on X-axis. The center of mass x CM can be obtained using equation 5.4. The point masses are at positions, x 1 = 4 m, x 2 = 8 m from the origin along X axis. Let us take, m 1 = 3 kg and m 2 = 5 kg (i) To find center of mass from the origin: Locate the position of center of mass of the two point masses (i) from the origin and (ii) from 3 kg mass. Two point masses 3 kg and 5 kg are at 4 m and 8 m from the origin on X-axis. Solved Example Problems for Center of Mass of Two Point Masses Example 5.1


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
